Molecular species fingerprinting and quantitative analysis of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) for quality control by MALDI mass spectrometry†
Abstract
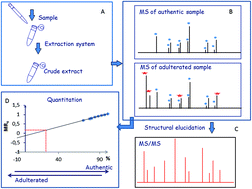
Herein we describe a rapid, simple, and reliable method for the quantitative analysis and molecular species fingerprinting of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) by direct MS and MS/MS analysis. Experimentally, powdered saffron was subjected to a brief treatment with a 0.3% TFA water/acetonitrile solution, and the resulting mixture was directly placed on the MALDI plate for analysis. This approach allowed the detection of the commonly observed crocins C-1–C-6 and flavonols, together with the identification of the unknown highly glycosylated crocins C-7, C-8 and C-9, and carotenoid-derived metabolites. The strategy endorsed the simultaneous detection and characterization of saffron and adulterant markers using crude extracts of the adulterant itself and synthetic sets of adulterated authentic saffron samples. The implementation of the strategy was to measure the amount of an unknown adulterant from the crude extract using curcumin as a non-isotopic isobaric internal standard. The relationship between the saffron and curcumin molar ratios were established with a correlation coefficient of 0.9942. The ANOVA regression model was significant, F(1, 72) = 13 595.82, p < 0.001, y = (0.0116 ± 0.0001)x + (−0.1214 ± 0.0086). No matrix effects were observed and good results were obtained with respect to instrumental repeatability (*RSD% < 2%) and LOD (1.1%). The analysis of commercial samples of saffron using the proposed approach showed the suitability of the method for routine analysis (minimal sample preparation and very short measuring time per sample).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...