Polydopamine-based nanoparticles with excellent biocompatibility for photothermally enhanced gene delivery
Abstract
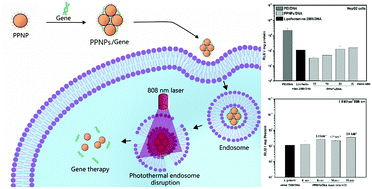
For non-viral gene delivery systems, desirable endosomal release is crucial for the achievement of optimum therapeutic efficacy. In this work, polyethylenimine-modified polydopamine-based nanoparticles (PPNPs) with excellent biocompatibility were prepared. These PPNPs showed an average diameter of 13 nm with narrow size distribution. Besides, they could load pGL3 DNA effectively at a mass ratio of PPNPs to DNA above 5 and form complexes with spherical morphology (60–80 nm). And PPNPs/DNA complexes demonstrated good photothermal conversion ability. Due to the excellent biocompatibility of polydopamine, these PPNPs/DNA complexes showed low cytotoxicity to HepG2 cells, even after 15 minutes of NIR light irradiation. Furthermore, the PPNPs/DNA complexes with mass ratios of 23 and 30 showed higher transfection levels than Lipofectamine 2000. After exposing these complexes to near infrared (NIR) light with a power density of 2.6 W cm−2 for 15 min, the transfection level of PPNPs/DNA complexes tripled in HepG2 cells. The rise in gene transfection was attributed to the locally induced heat produced by the PPNPs/DNA complexes, which promoted endosomal membrane disruption and led to better endosomal escape. This result was also confirmed by confocal laser scanning microscope observation. Moreover, PPNPs/DNA complexes demonstrated excellent biocompatibility in hemolysis assays. At the mass ratio of 23 and DNA concentration of 20 μg mL−1, the hemolysis ratio of the PPNPs/DNA complexes was only 1%, lower than that of the PEI/DNA complexes. This PPNP nanocarrier was inspiring for the design of non-viral gene delivery systems with promoted therapeutic efficacy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...