Comparative analysis on adsorption properties and mechanisms of nitrate and phosphate by modified corn stalks†
Abstract
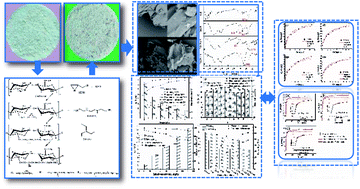
In this study, modified corn stalks (MCS) were successfully synthesized by grafting or crosslinking triethylenetetramine (TETA) and triethylamine (TEA) in the presence of epichlorohydrin (EPI) and N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) for the effective removal of nitrate and phosphate. The characteristics of adsorbents were determined and the adsorption properties and mechanisms of nitrate and phosphate on MCS were studied and compared. Results from Zeta potential, elemental analysis (EA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) showed that quaternary ammonium group was successfully grafted onto corn stalks (CS). Both adsorption properties and mechanisms indicated that the MCS had a better affinity to phosphate. For adsorption properties, under conditions of a dosage of 4 g L−1, pH 6.0 and an initial concentration of 50 mg L−1, the phosphate removal rate was 10.97% higher than that nitrate, and SO42− and Cl− had a larger inhibitive effect on nitrate. Mechanisms analysis included adsorption kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics. Results indicated that the parameters of different models were closely related to the adsorption effect of nitrate and phosphate. In addition, pseudo-second-order and Freundlich model fitted both nitrate and phosphate adsorption well. The thermodynamics analysis indicated that the adsorption process was spontaneous and endothermic in nature.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...