Chemical bond parameters, bond energy and the local crystal sites of Eu3+ in Ca5(BO3)3F:1% Eu3+ phosphor
Abstract
The local crystal sites occupied by Eu3+ in Ca5(BO3)3F:1% Eu3+ phosphor were investigated experimentally and theoretically. Ca5(BO3)3F:1% Eu3+ was synthesized by high-temperature solid-state method in air. The crystal structure and optical properties of the phosphor were studied by X-ray powder diffraction and photoluminescence, respectively. Two different O2− → Eu3+ CT broad bands with the peaks at 266 and 283 nm in Ca5(BO3)3F:1% Eu3+ were detected, indicating the Eu3+ sites occupied Ca2 and Ca1, respectively. The different sharp f–f emission spectra under the excitation of 283 and 266 nm proved that there are two different local lattice environments around Eu3+ existing in Ca5(BO3)3F:1% Eu3+. Environmental factor he, the standard deviation of environmental factor (EFSD) 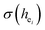 and the bond energy were used to illustrate and explain the site occupancy mechanism of Eu3+ into the host lattice. By comparing the intensity ratios of 5D0 → 7F2 transition to the 5D0 → 7F1 transition, I(5D0/7F2)/I(5D0/7F1) of Eu3+ at Ca2 (7.381) was found to be 2.5 times stronger than that of Eu3+ at Ca1 site (2.933).
and the bond energy were used to illustrate and explain the site occupancy mechanism of Eu3+ into the host lattice. By comparing the intensity ratios of 5D0 → 7F2 transition to the 5D0 → 7F1 transition, I(5D0/7F2)/I(5D0/7F1) of Eu3+ at Ca2 (7.381) was found to be 2.5 times stronger than that of Eu3+ at Ca1 site (2.933). 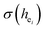 was calculated to analyze the I(5D0/7F2)/I(5D0/7F1) value. On the basis of the bond valence model, a bond-energy method was used to study the occupancy of the Eu ion, which indicated that the preferential sites of Eu ion occupancy in the Ca5(BO3)3F are the Ca2 and Ca1 sites. All three theoretical calculation results are consistent with each other.
was calculated to analyze the I(5D0/7F2)/I(5D0/7F1) value. On the basis of the bond valence model, a bond-energy method was used to study the occupancy of the Eu ion, which indicated that the preferential sites of Eu ion occupancy in the Ca5(BO3)3F are the Ca2 and Ca1 sites. All three theoretical calculation results are consistent with each other.



 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...