Hollow silica capsules for amphiphilic transport and sustained delivery of antibiotic and anticancer drugs
Abstract
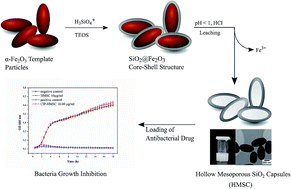
Hollow mesoporous silica capsules (HMSC) are potential drug transport vehicles due to their biocompatibility, high loading capacity and sufficient stability in biological milieu. Herein, we report the synthesis of ellipsoid-shaped HMSC (aspect ratio ∼2) performed using hematite particles as solid templates that were coated with a conformal silica shell through cross-condensation reactions. For obtaining hollow silica capsules, the iron oxide core was removed by acidic leaching. Gas sorption studies on HMSC revealed mesoscopic pores (main pore width ∼38 Å) and a high surface area of 308.8 m2 g−1. Cell uptake of dye-labeled HMSC was confirmed by incubating them with human cervical cancer (HeLa) cells and analyzing the internalization through confocal microscopy. The amphiphilic nature of HMSC for drug delivery applications was tested by loading antibiotic (ciprofloxacin) and anticancer (curcumin) compounds as model drugs for hydrophilic and hydrophobic therapeutics, respectively. The versatility of HMSC in transporting hydrophilic as well as hydrophobic drugs and a pH dependent drug release over several days under physiological conditions was demonstrated in both cases by UV-vis spectroscopy. Ciprofloxacin-loaded HMSC were additionally evaluated towards Gram negative (E. coli) bacteria and demonstrated their efficacy even at low concentrations (10 μg ml−1) in inhibiting complete bacterial growth over 18 hours.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...