LiMg0.1Co0.9BO3 as a positive electrode material for Li-ion batteries†
Abstract
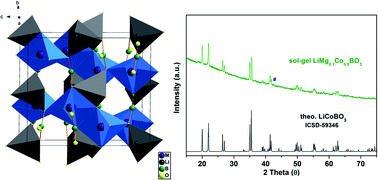
LiCoBO3 could be a promising cathode material given the electronic and ionic conductivity problems are addressed. Here, Mg substitution in LiCoBO3 is employed to stabilise the structure and improve the electrochemical performance. LiMg0.1Co0.9BO3 is synthesised for the first time via sol–gel method and Mg substitution in the structure is verified by X-ray powder diffraction and energy dispersive X-ray analyses. The electrochemical properties are investigated by galvanostatic cycling and cyclic voltammetry tests. The composite electrode with conductive carbon (reduced graphite oxide and carbon black) delivers a first discharge capacity of 32 mA h g−1 within a 4.7–1.7 voltage window at a rate of 10 mA g−1. The cycling is relatively stable compared to the unsubstituted LiCoBO3. Mg substitution may enhance the electrochemical performance of borate-based electrode materials when combined with suitable electrode design techniques.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...