Study on the degradation mechanism and pathway of benzene dye intermediate 4-methoxy-2-nitroaniline via multiple methods in Fenton oxidation process
Abstract
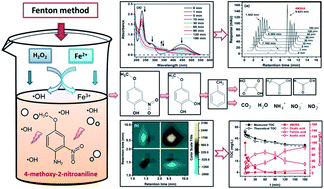
Benzene dye intermediate (BDI) 4-methoxy-2-nitroaniline (4M2NA) wastewater has caused significant environmental concern due to its strong toxicity and potential carcinogenic effects. Reports concerning the degradation of 4M2NA by advanced oxidation process are limited. In this study, 4M2NA degradation by Fenton oxidation has been studied to obtain more insights into the reaction mechanism involved in the oxidation of 4M2NA. Results showed that when the 4M2NA (100 mg L−1) was completely decomposed, the TOC removal efficiency was only 30.70–31.54%, suggesting that some by-products highly recalcitrant to the Fenton oxidation were produced. UV-Vis spectra analysis based on Gauss peak fitting, HPLC analysis combined with two-dimensional correlation spectroscopy and GC-MS detection were carried out to clarify the degradation mechanism and pathway of 4M2NA. A total of nineteen reaction intermediates were identified and two possible degradation pathways were illustrated. Theoretical TOC calculated based on the concentration of oxalic acid, acetic acid, formic acid, and 4M2NA in the degradation process was nearly 94.41–97.11% of the measured TOC, indicating that the oxalic acid, acetic acid and formic acid were the main products. Finally, the predominant degradation pathway was proposed. These results could provide significant information to better understand the degradation mechanism of 4M2NA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...