Effect of organic ligand-decorated ZnO nanoparticles as a cathode buffer layer on electricity conversion efficiency of an inverted solar cell
Abstract
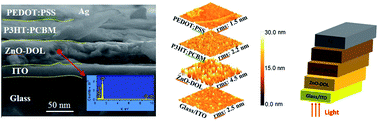
Efficiency improvement of the industrial scale solar cells to capture sunlight as an important renewable energy source is attracting significant attention to prevent the consumption of a finite supply of unsustainable fossil fuels. ZnO nanoparticles decorated with an imine-linked receptor have been used in the fabrication of a photocathode based on dye-sensitized solar cells for the purpose of photovoltaic efficiency enhancement. Various characterization techniques have been employed to investigate the structural, morphological, and optical behaviors of the solar cell having ZnO nanoparticles and ZnO nanoparticles decorated with an organic ligand as a photocathode layer. The decorated nanoparticles have a stable wurtzite structure and an average grain size of ∼45 nm, confirmed by the TEM image and XRD through the Scherrer equation. The ZnO sample emits wide peaks in the visible range, and the emission intensity of the ZnO-DOL sample increases along with a red-shift (0.38 eV) in the band gap. This shift can be explained using deep level transition, surface plasmon energy of a surfactant, and coupling of ZnO with local surface plasmon energy. UV-vis absorption spectra together with photoluminescence spectra confirm the higher absorption rate due to organic ligand decoration on ZnO nanoparticles. The greatest solar power-to-electricity conversion efficiency (η) of 3.48% is achieved for the ZnO-DOL sample. It is enhanced by 3.13% as compared to that of the ZnO-based solar cell. The ZnO-DOL device exhibits a higher external quantum efficiency (EQE), responsivity (Rλ), and photocurrent-to-dark current ratio; this confirms the improvement in the solar cell performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...