Graphene oxide-modified LaVO4 nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic degradation efficiency of antibiotics†
Abstract
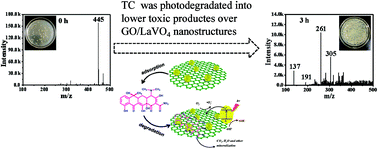
The rational design of green and stable photocatalysts applied for highly efficient removal of antibiotics still remains a great challenge. In particular, the systematic analysis of the degradation pathway and toxicity of antibiotic degradation products is essential, but only few studies have been reported. Herein, novel GO/LaVO4 composite materials were fabricated via a facile one-step hydrothermal method, which presented enhanced photocatalytic degradation efficiency for tetracycline (TC) and naproxen (NPX) under visible light irradiation. It was found that 0.01% GO/LaVO4 presented the highest degradation rate with good stability, which is 3.46-times (for TC) and 2.29-times (for NPX) compared with that pure LaVO4. In particular, it is worth mentioning that the intermediates of TC produced during the photodegradation reaction and the corresponding possible degradation pathway were analyzed in depth by mass spectrometry (MS). More importantly, through the design of toxicology experiments, the toxicity of the TC solution was eliminated after the photocatalytic treatment. These results indicated that the modification of GO could efficiently improve the optical absorption property and accelerate the separation and migration of photogenerated charge carriers, thus enhancing the photocatalytic activity. This study offers a new perspective on the design of other LaVO4-based photocatalysts for efficient antibiotics’ removal.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...