An in situ study on the solid state decomposition of ammonia borane: unmitigated by-product suppression by a naturally abundant layered clay mineral†
Abstract
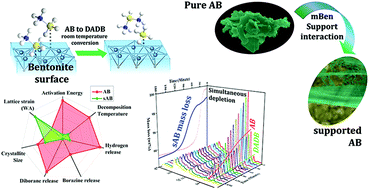
Borazine is a by-product often encountered in the thermal decomposition of ammonia borane, which leads to an inescapable hindrance towards sustainability and cost effectiveness. In this study, a low cost, low surface area clay mineral, bentonite, was modified and introduced as a support material. Bentonite (42.4 m2 g−1) revealed decomposition characteristics comparable to previously reported high surface area (usually 700–1000 m2 g−1) support materials. In addition, borazine formation from bentonite supported ammonia borane was observed to be completely eliminated. Extensive size strain analysis (Williamson–Hall and Warren–Averbach) indicated that the crystalline parameters were observed to be a considerable factor affecting the dehydrogenation reaction along with the high surface area. However, using in situ XRD and MS characterization, the supported decomposition was attributed to a facile pathway, which was dominated by DADB formation. The proposed pathway justifies the borazine elimination and more steady hydrogen release from AB.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...