Coordinative chain transfer copolymerization of ethylene and styrene using an ansa-bis(fluorenyl) neodymium complex and dialkylmagnesium†
Abstract
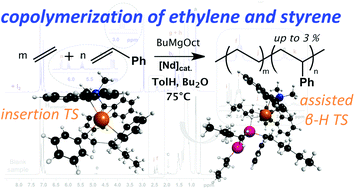
Coordinative chain transfer copolymerization of ethylene and styrene was successfully achieved using an ansa-bisfluorenyl neodymium complex, a dialkylmagnesium as a chain transfer agent and di-n-butylether (Bu2O) as a co-solvent. Under these conditions, a controlled chain growth was observed during the polymerization. Chain-end functionalization was performed and it revealed that both styryl and alkyl terminated chains shuttle between neodymium and magnesium. The analysis of the microstructure revealed that up to 3 mol% of styrene can be incorporated into the polymer. A computational mechanistic study at the DFT level was performed to characterize insertion selectivities and it further revealed the role of magnesium species in assisting β-H elimination.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...