Design and characterization of ultrastable, biopassive and lubricious cyclic poly(2-alkyl-2-oxazoline) brushes†
Abstract
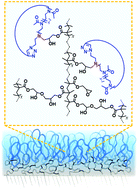
Bilayer polymer brushes presenting surface-bound poly(glycidyl methacrylate) (PGMA) films and interfacial cyclic poly(2-alkyl-2-oxazoline) (PAOXA) brushes show excellent biopassivity and lubrication, while displaying long-term stability in chemically harsh aqueous environments. Due to their lower radii of gyration (Rg), cyclic poly(2-methyl-2-oxazoline)s (PMOXAs) and poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)s (PEOXAs) react at high temperatures with PGMA grafts producing ∼50% denser brushes compared to linear analogues featuring comparable molar masses. This generates significantly more hydrated brush interfaces, which quantitatively prevent unspecific surface contamination by biomolecules after several hours of exposure. In addition, the more compact and denser character of cyclic brushes imparts excellent lubricating properties to the bilayered coatings, with the more hydrophilic cyclic PMOXA interfaces reaching a coefficient of friction (μ) of 0.05 against a silica AFM probe in aqueous medium. In addition to their unique physicochemical properties, cyclic PMOXA and PEOXA brushes grafted on PGMA layers demonstrate extremely robust films, which could withstand one month incubation in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) solution, tap water or water from Lake Zurich.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...