Photobiomodulation prevents DNA fragmentation of alveolar epithelial cells and alters the mRNA levels of caspase 3 and Bcl-2 genes in acute lung injury
Abstract
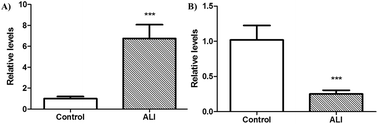
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and acute lung injury (ALI) are defined as pulmonary inflammation that could occur from sepsis and lead to pulmonary permeability and alveolar edema making them life-threatening diseases. Photobiomodulation (PBM) properties have been widely described in the literature in several inflammatory diseases; although the mechanisms of action are not always clear, this could be a possible treatment for ARDS/ALI. Thus, the aim of this study was to evaluate the mRNA levels from caspase-3 and BCL-2 genes and DNA fragmentation in lung tissue from Wistar rats affected by ALI and subjected to photobiomodulation by exposure to a low power infrared laser (808 nm; 100 mW; 3.571 W cm−2; four points per lung). Adult male Wistar rats were randomized into 6 groups (n = 5, for each group): control, PBM10 (10 J cm−2, 2 J and 2 seconds), PBM20 (20 J cm−2, 5 J and 5 seconds), ALI, ALI + PBM10 and ALI + PBM20. ALI was induced by intraperitoneal Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide injection. Lung samples were collected and divided for mRNA expression of caspase-3 and Bcl-2 and DNA fragmentation quantifications. Data show that caspase-3 mRNA levels are reduced and Bcl-2 mRNA levels increased in ALI after low power infrared laser exposure when compared to the non-exposed ALI group. DNA fragmentation increased in inflammatory infiltrate cells and reduced in alveolar cells. Our research shows that photobiomodulation can alter relative mRNA levels in genes involved in the apoptotic process and DNA fragmentation in inflammatory and alveolar cells after lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Also, inflammatory cell apoptosis is part of the photobiomodulation effects induced by exposure to a low power infrared laser.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...