Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction of a chiral aziridine aldehyde†
Abstract
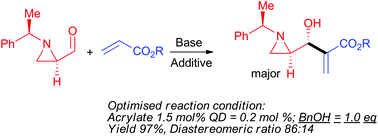
The Morita–Baylis–Hillman reaction of (R)-1-((R)-1-phenylethyl)aziridine-2-carbaldehyde with alkyl acrylate was carried out under various conditions by changing solvents, bases, and alcohol additives. The reaction at room temperature under neat conditions (no solvent) with quinuclidine as an amine nucleophile, in the presence of benzyl alcohol as an additive, afforded a product, γ-(aziridin-2-yl)-β-hydroxy-α-methylene butanoate, in 97% yield with a diastereomeric ratio of anti and syn as 86 : 14.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Synthetic methodology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...