Copper-catalyzed oxidative cross-dehydrogenative coupling of 2H-chromenes and terminal alkynes†
Abstract
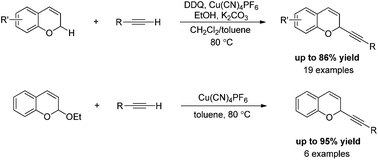
An efficient copper-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenative coupling of 2H-chromenes and terminal alkynes mediated by DDQ has been established. A protic additive, EtOH, proved to be crucial for harmonizing the oxidation with a subsequent alkynylation step by retaining the oxidation state of an oxocarbenium ion in the form of acetal. The CDC reaction exhibits a good substrate scope, with a range of terminal aryl- and alkyl alkynes being well tolerated. The copper-catalyzed alkynylation of 2H-chromene acetals with terminal alkynes was also explored.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Synthetic methodology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...