On the ozonolysis of unsaturated tosylhydrazones as a direct approach to diazocarbonyl compounds†
Abstract
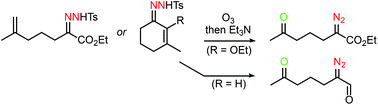
The scope and limitations are described of reacting unsaturated tosylhydrazones with O3 followed by Et3N for the generation of 1,4- and 1,5-diazocarbonyl systems. Tosylhydrazones, from tosylhydrazide condensation with readily available δ- and ε-unsaturated α-ketoesters, led in the former case to a 2-pyrazoline whereas the latter cases led to α-diazo-ε-ketoesters, although a terminal alkene produced a tetrahydropyridazinol. Using the ozonolysis–Et3N strategy, tosylhydrazones from cyclic enones give 2,5- and 2,6-diazoketones with aldehyde or ester functionality at the 1-position; the α-diazoaldehydes prefer the s-trans conformation, with a rotation barrier of 74 kJ mol−1 at 25 °C determined by NMR. This one-pot ozonolysis/Bamford–Stevens chemistry demonstrates both the tolerance of tosylhydrazones to ozone, and the subsequently added amine playing a dual role to directly transform the intermediate tosylhydrazone ozonides into products containing reactive diazo and ketone functionalities; such adducts are of particular value as precursors to cyclic carbonyl ylides for 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Synthetic methodology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...