Ancistrocyclinones A and B, unprecedented pentacyclic N,C-coupled naphthylisoquinoline alkaloids, from the Chinese liana Ancistrocladus tectorius†‡
Abstract
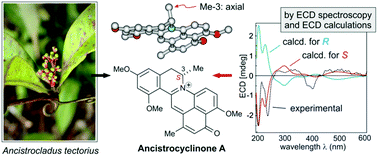
Two unique pentacyclic N,C-coupled naphthylisoquinolines, the ancistrocyclinones A (5) and B (6), were discovered in the Chinese liana Ancistrocladus tectorius. Furthermore, six known, likewise N,C-coupled alkaloids, viz., ancistrocladinium A (7a) and its mono- and bisphenolic analogs 8a and 9a were isolated, along with their atropo-diastereomers 7b, 8b, and 9b. The stereostructures of 5 and 6 were determined by HRESIMS, 1D and 2D NMR, oxidative degradation, and ECD calculations. The pentacyclic ancistrocyclinones A (5) and B (6) are structurally similar to berberine alkaloids – yet arising from a most different biosynthetic pathway: they are apparently formed by N,C-coupling of their polyketide-derived molecular halves, followed by oxidative cyclo-condensation. Biomimetic conversion of the co-occurring 4′-O-demethylancistrocladinium A (8a) to ancistrocyclinone A (5) via a quinoid intermediate supported the postulated pathway. Ancistrocyclinone A (5) was found to significantly inhibit the viability of drug-sensitive human leukemia (CCRF-CEM) and multidrug-resistant tumor cells (CEM/ADR5000) with comparable efficacies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...