Differentiation of enantiomeric anions by NMR spectroscopy with chiral bisurea receptors†
Abstract
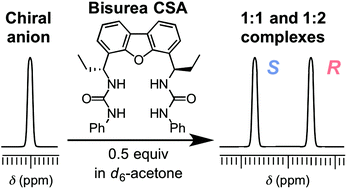
Chiral anionic species are ubiquitous and play important roles in biological systems. Despite the recent advancements in synthetic anion receptors bearing urea functionalities, urea-based chiral solvating agents (CSAs) that can separate the NMR signals of racemic anions remain limited. Herein, three dibenzofuran-based C2-symmetric chiral bisureas were synthesized from the reaction of (R,R)-4,6-bis(1-aminopropyl)dibenzo[b,d]furan with phenyl isocyanate, phenyl thioisocyanate, or tosyl isocyanate. The chiral anion recognition properties of these bisureas were examined by 1H NMR spectroscopy using DL-tetrabutylammonium mandelate (TBAM) as a model substrate. A clear baseline separation of the enantiomeric signals of the benzylic proton of TBAM was achieved upon mixing with 0.5 equivalents of bis(phenylurea). In contrast to previous urea-based chiral anion receptors that differentiate the enantiomers of chiral anions by forming 1 : 1 host–guest complexes, a high chiral recognition ability of chiral bis(phenylurea) was achieved owing to the generation of an equilibrium between free guests, 1 : 1 host–guest complexes, and 1 : 2 host–guest complexes. Chiral bis(phenylurea) was also successfully employed in the separation of the enantiomeric 1H NMR signals of various racemic anions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...