Graphene quantum dots against human IAPP aggregation and toxicity in vivo†
Abstract
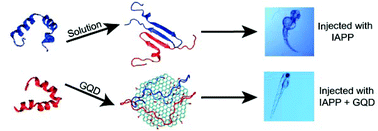
The development of biocompatible nanomaterials has become a new frontier in the detection, treatment and prevention of human amyloid diseases. Here we demonstrated the use of graphene quantum dots (GQDs) as a potent inhibitor against the in vivo aggregation and toxicity of human islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP), a hallmark of type 2 diabetes. GQDs initiated contact with IAPP through electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions as well as hydrogen bonding, which subsequently drove the peptide fibrillization off-pathway to eliminate the toxic intermediates. Such interactions, probed in vitro by a thioflavin T kinetic assay, fluorescence quenching, circular dichroism spectroscopy, a cell viability assay and in silico by discrete molecular dynamics simulations, translated to a significant recovery of embryonic zebrafish from the damage elicited by IAPP in vivo, as indicated by improved hatching as well as alleviated reactive oxygen species production, abnormality and mortality of the organism. This study points to the potential of using zero-dimensional nanomaterials for in vivo mitigation of a range of amyloidosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...