Large tunneling magnetoresistance in magnetic tunneling junctions based on two-dimensional CrX3 (X = Br, I) monolayers†
Abstract
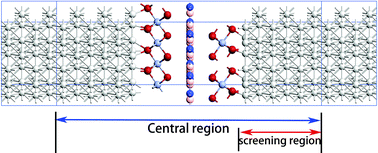
Magnetic tunneling junctions (MTJs) have atomic thickness due to the use of two-dimensional (2D) materials. Combining density functional theory with non-equilibrium Green's function formalism, we systematically investigate the structural and magnetic properties of CrX3/h-BN/CrX3 (X = Br, I) MTJs, as well as their spin-dependent transport characteristics. Through calculation of the transmission spectrum, the large tunneling magnetoresistance (TMR) effect was observed in these MTJs. Moreover, their conductance based on two-dimensional materials was greatly improved over that of traditional MTJs. The transmission mechanism was analyzed using the symmetry of the orbit and the eigenstates of the transmitted electrons. We also discuss the problem of Schottky contact between different metal electrodes and devices. Our results suggest that MTJs based on two-dimensional ferromagnets are feasible.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...