Pt alloy nanoparticles decorated on large-size nitrogen-doped graphene tubes for highly stable oxygen-reduction catalysts†
Abstract
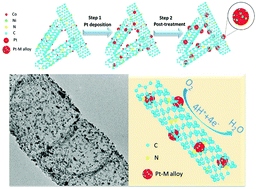
Pt alloy nanoparticles supported on Vulcan XC-72 (Pt/C) are the most effective catalysts for kinetically sluggish oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. However, significant performance degradation has been observed with the Pt/C catalysts due to agglomeration and Ostwald ripening of Pt nanoparticles largely resulting from the corrosion of carbon supports. Here, we developed a Pt alloy catalyst through annealing Pt nanoparticles deposited on nitrogen/metal co-doped large-size graphene tubes (NGTs). The in-situ formation of PtM (M: Co and Ni) alloy during the annealing process contributes to the improvement of the catalytic activity and stability. During the accelerated stress tests (AST), after 20 000 potential cycles (0.6–1.0 V vs. RHE), the retained electrochemical surface area (ECSA) of the PtM/NGT catalyst is more than 2 times larger than that of the Pt/C catalyst. As for the AST tests of carbon corrosion, after 30 000 potential cycles (1.0–1.5 V vs. RHE) at room temperature, the NGT morphologies are well maintained and no ECSA loss of this PtM catalyst is observed, indicating excellent corrosion-resistance. Even at harsher 60 °C, the PtM/NGT catalyst exhibits only insignificant loss (6 mV) of E1/2 while the Pt/C catalyst shows significant degradation (47 mV loss in E1/2). The improved stability of PtM/NGT catalyst is attributed to the highly graphitized NGTs and possible synergistic effects between the NGT carbon support and the PtM alloy nanoparticles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...