Multi-layer nanoarrays sandwiched by anodized aluminium oxide membranes: an approach to an inexpensive, reproducible, highly sensitive SERS substrate†
Abstract
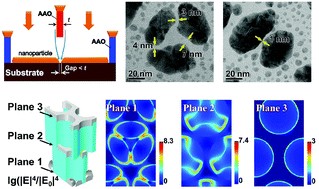
A large-scale sub-5 nm nanofabrication technique is developed based on double layer anodized aluminium oxide (AAO) porous membrane masking. This technique also provides a facile route to form multilayer nano-arrays (metal nanoarrays sandwiched by AAO membranes), which is very challenging for other techniques. Normally the AAO mask has to be sacrificed, yet in this work it is preserved as a part of the nanostructure. The preserved AAO layers as the support for the second/third layer of the metal arrays provide a high-refractive index background for the multilayer metal arrays. This background concentrates the local E-field more significantly and results in a much higher Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) signal than single layer metal arrays. This technique may lead to the advent of an inexpensive, reproducible, highly sensitive SERS substrate. Moreover, the physical essence of the plasmonic enhancement is unveiled by finite element method based numerical simulations. Enhancements from the gaps and the multilayer nanostructure agree very well with the experiments. The calculated layer-by-layer electric field distribution determines the contribution from different layers and provides more insights into the 3D textured structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...