Distinct roles of SNARE-mimicking lipopeptides during initial steps of membrane fusion†
Abstract
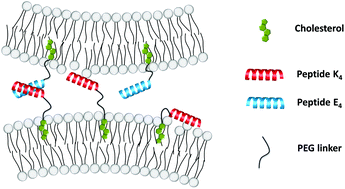
A model system for membrane fusion, inspired by SNARE proteins and based on two complementary lipopeptides CPnE4 and CPnK4, has been recently developed. It consists of cholesterol (C), a poly(ethylene glycol) linker (Pn) and either a cationic peptide K4 (KIAALKE)4 or an anionic peptide E4 (EIAALEK)4. In this paper, fluorescence spectroscopy is used to decipher distinct but complementary roles of these lipopeptides during early stages of membrane fusion. Molecular evidence is provided that different distances of E4 in CPnE4 and K4 in CPnK4 from the bilayer represent an important mechanism, which enables fusion. Whereas E4 is exposed to the bulk and solely promotes membrane binding of CPnK4, K4 loops back to the lipid–water interface where it fulfills two distinct roles: it initiates bilayer contact by binding to CPnE4 containing bilayers; and it initiates fusion by modulating the bilayer properties. The interaction between CPnE4 and CPnK4 is severely down-regulated by binding of K4 to the bilayer and possible only if the lipopeptides approach each other as constituents of different bilayers. When the complementary lipopeptides are localized in the same bilayer, hetero-coiling is disabled. These data provide crucial insights as to how fusion is initiated and highlight the importance of both peptides in this process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...