Enhanced capture and release of circulating tumor cells using hollow glass microspheres with a nanostructured surface†
Abstract
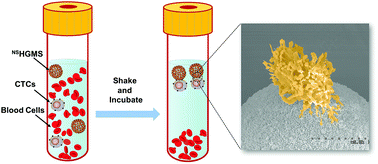
Self-floating hollow glass microspheres (HGMS) modified with tumor-specific antibodies have been developed for the capture of circulating tumor cells (CTCs), and have demonstrated effective cell isolation and good viability of isolated cancer cells. However, the capture efficiency decreases dramatically if the spiked cell concentration is low, possibly due to insufficient interactions between cancer cells and the HGMS surface. In order to apply HGMS-based CTC isolation to clinically relevant samples, it is desirable to create nanostructures on the surface of HGMS to enhance cell-surface interactions. Nevertheless, current microfabrication methods cannot generate nanostructured-surfaces on microspheres. The authors have developed a new HGMS with a controlled nanotopographical surface structure (NSHGMS), and demonstrated isolation and recovery of rare cancer cells. NSHGMS are achieved by applying layer-by-layer (LbL) assembly of negatively charged SiO2 nanoparticles and positively charged poly-L-arginine molecules, then sheathing the surface with an enzymatically degradable LbL film made from biotinylated alginate and poly-L-arginine, and capping with anti-EpCAM antibodies and anti-fouling PEG molecules. Compared to smooth-surfaced HGMS, NSHGMS showed shorter isolation time (20 min), enhanced capture efficiency (93.6 ± 4.9%) and lower detection limit (30 cells per mL) for commonly used cancer cell lines (MCF7, SK-BR-3, PC-3, A549 and CCRF-CEM). This NSHGMS-based CTC isolation method does not require specialized lab equipment or an external power source, and thus, can be used for the separation of targeted cells from blood or other body fluids in a resource-limited environment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...