Bortezomib-catechol conjugated prodrug micelles: combining bone targeting and aryl boronate-based pH-responsive drug release for cancer bone-metastasis therapy†
Abstract
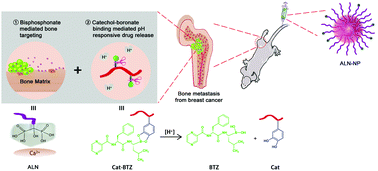
The treatment of metastatic tumors is highly desirable in clinics, which has also increased the interest in the design of nanoscale drug delivery systems. Bone metastasis is one of the most common pathways in the metastasis of breast cancer, and it is also an important cause for tumor recurrence and death. The aryl boronate group, as an acid-labile linker, has been introduced into nano-assemblies in recent years. Especially, as a proteasome inhibitor anticancer drug with a boric acid group, bortezomib can facilitate the formation of pH-sensitive aryl boric acid ester linkage with the catecholic group. In this study, bortezomib-loaded micelles with bone targeting properties were constructed for the treatment of breast cancer bone metastasis. The mixed micelles employed alendronate (ALN) as the bone-targeting ligand and encapsulated bortezomib-catechol conjugates as the cargo. In vitro and in vivo studies showed that compared with free drugs or control micelles, these prodrug micelles (ALN-NP) exhibited many favorable properties such as reduced systemic toxicity and improved therapeutic effects. Therefore, ALN-NP is promising as a nanovehicle for bone-targeting delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs. Furthermore, this study offers a novel strategy combining bone targeting and aryl boronate-based pH-responsive drug release for anti-metastasis therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...