Fluorescent and photoacoustic bifunctional probe for the detection of ascorbic acid in biological fluids, living cells and in vivo†
Abstract
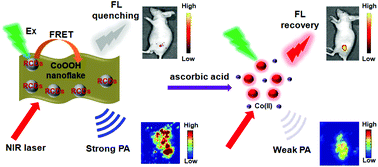
Photoacoustic imaging (PAI) has emerged as a promising clinical technology, thanks to its high-resolution in deep tissues. However, the lack of specificity towards analytes limits further application of the PA probe in molecular imaging. To this end, we herein report a PA and fluorescence (FL) dual-modal probe for the selective detection of ascorbic acid (AA). To realize this design, cobalt oxyhydroxide (CoOOH) was adopted as a multifunctional platform (PA contrast agent, FL quencher and specific oxidant to AA) and hybridized with red-emissive carbon dots (RCDs). In the presence of AA, CoOOH is reduced to Co2+ and meanwhile releases RCDs, resulting in the decrease of PA and recovery of FL signals. We demonstrated the AA detection capabilities of the probe in complicated biological fluids (human serum and urine), living cells, and dual-modal FL/PA imaging in vivo. This work revealed the PAI capacity of CoOOH for the first time, which may inspire researchers to design other CoOOH-based PA probes and further employ RCDs in biology and the clinic.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...