A dimorphism shift of hepatitis B virus capsids in response to ionic conditions†
Abstract
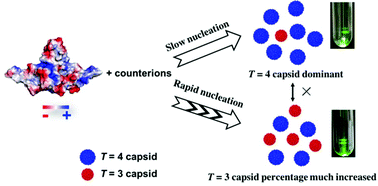
The dimorphism of HBV capsids (coexistence of T = 3 and T = 4 capsids) was found to be regulatable by controlling the rate of capsid nucleation using cations such as K+ or Ca2+: a quick addition of highly concentrated monovalent and/or multivalent counter-cations resulted in a morphism transition from a thermodynamically more stable, T = 4 capsid-dominant state (>80% of total capsids) to a new state containing ∼1 : 1 amounts of T = 3 and T = 4 capsids. These results suggested that the salts with strong charge screening ability could narrow the difference in nucleation energy barriers between the two states, which were not inter-convertible once formed. The effect of salts was more significant than other factors such as pH or protein concentration in achieving such a dimorphism shift. The general mechanism of HBV capsid dimorphism described here provides a new perspective in understanding the virus assembly during infection and directing the design of non-infectious capsids for nanotechnology applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...