A long-chain protic ionic liquid inside silica nanopores: enhanced proton mobility due to efficient self-assembly and decoupled proton transport†
Abstract
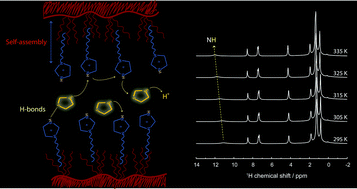
We report enhanced protonic and ionic dynamics in an imidazole/protic ionic liquid mixture confined within the nanopores of silica particles. The ionic liquid is 1-octylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([HC8Im][TFSI]), while the silica particles are microsized and characterized by internal well connected nanopores. We demonstrate that the addition of imidazole is crucial to promote a proton motion decoupled from molecular diffusion, which occurs due to the establishment of new N–H⋯N hydrogen bonds and fast proton exchange events in the ionic domains, as evidenced by both infrared and 1H NMR spectroscopy. An additional reason for the decoupled motion of protons is the nanosegregated structure adopted by the liquid imidazole/[HC8Im][TFSI] mixture, with segregated polar and non-polar nano-domains, as clearly shown by WAXS data. This arrangement, promoted by the length of the octyl group and thus by significant chain–chain interactions, reduces the mobility of molecules (Dmol) more than that of protons (DH), which is manifested by DH/Dmol ratios greater than three. Once included into the nanopores of hydrophobic silica microparticles, the nanostructure of the liquid mixture is preserved with slightly larger ionic domains, but effects on the non-polar ones are unclear. This results in a further enhancement of proton motion with localised paths of conduction. These findings demonstrate significant progress in the design of proton conducting materials via tailor-made molecular structures as well as by smart exploitation of confinement effects. Compared to other imidazole-based proton conducting materials that are crystalline up to 90 °C or above, the gel materials that we propose are useful for applications at room temperature, and can thus find applications in e.g. intermediate temperature proton exchange fuel cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...