Covalently bonded multimers of Au25(SBut)18 as a conjugated system†
Abstract
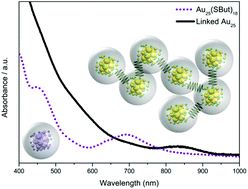
Aromatic dithiol linkers were used to prepare aggregates of Au25(SR)18 clusters (SR: thiolate) via ligand exchange reactions. Fractions of different aggregate sizes were separated by size exclusion chromatography (SEC). The aggregates were characterized by UV-vis absorption spectroscopy, matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy (including diffusion-ordered spectroscopy, DOSY) and small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). At a 2 : 1 cluster : dithiol ratio, small aggregates (dimers, trimers) and also larger aggregates consisting of 10–20 Au25 clusters were formed, according to DOSY, besides unreacted (monomeric) Au25(SR)18. MALDI mass spectrometry shows signals consistent with dimers and trimers (doubly charged). The SAXS curves for the small aggregates can be well fitted by a pearl-necklace model. For the bigger aggregates the SAXS curves evidence a characteristic separation distance between the clusters within the aggregates, which is imposed by the length of the linker. The SAXS curves of these larger aggregates can be well fitted with a core–shell sphere model with a sticky hard-sphere structure factor, in agreement with closely packed aggregates. The absorption spectra of smaller aggregates resemble those of individual Au25(SR)18 clusters; however, and most importantly, the larger aggregates show completely different, less structured spectra with a new band emerging at 840 nm. We assign this drastic change in the absorption spectra and the new band to the electronic coupling between the clusters through the all aromatic linker. In accordance with this view, the aggregates formed with a linker containing methylene groups, thus breaking conjugation, do not show the band at 840 nm. By the addition of monothiols to the larger aggregates their size can be reduced through an “unlinking” reaction. This reaction also affects the band at 840 nm, which moves to higher energy when reducing the aggregate size, as would be expected within a particle in a box model. The electronic coupling between the clusters through the linker is the basis for future applications in nanoelectronics.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...