Functionalized 2D nanomaterials with switchable binding to investigate graphene–bacteria interactions†
Abstract
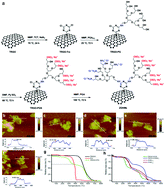
Graphene and its derivatives have recently attracted much attention for sensing and deactivating pathogens. However, the mechanism of multivalent interactions at the graphene–pathogen interface is not fully understood. Since different physicochemical parameters of graphene play a role at this interface, control over graphene's structure is necessary to study the mechanism of these interactions. In this work, different graphene derivatives and also zwitterionic graphene nanomaterials (ZGNMs) were synthesized with defined exposure, in terms of polymer coverage and functionality, and isoelectric points. Then, the switchable interactions of these nanomaterials with E. coli and Bacillus cereus were investigated to study the validity of the generally proposed “trapping” and “nano-knives” mechanisms for inactivating bacteria by graphene derivatives. It was found that the antibacterial activity of graphene derivatives strongly depends on the accessible area, i.e. edges and basal plane of sheets and tightness of their agglomerations. Our data clearly confirm the authenticity of “trapping” and “nano-knives” mechanisms for the antibacterial activity of graphene sheets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...