Biodistribution studies of ultrasmall silicon nanoparticles and carbon dots in experimental rats and tumor mice†
Abstract
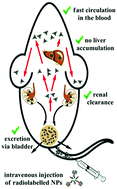
Ultrasmall clearable nanoparticles possess enormous potential as cancer imaging agents. In particular, biocompatible silicon nanoparticles (Si NPs) and carbon quantum dots (CQDs) hold great potential in this regard. Their facile surface functionalization easily allows the introduction of different labels for in vivo imaging. However, to date, a thorough biodistribution study by in vivo positron emission tomography (PET) and a comparative study of Si vs. C particles of similar size are missing. In this contribution, ultrasmall (size <5 nm) Si NPs and CQDs were synthesized and characterized by high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR), absorption and steady-state emission spectroscopy. Subsequent functionalization of NPs with a near-infrared dye (Kodak-XS-670) or a radiolabel (64Cu) enabled a detailed in vitro and in vivo study of the particles. For radiolabeling experiments, the bifunctional chelating agent S-2-(4-isothiocyanatobenzyl)-1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid (p-SCN-Bn-NOTA) was conjugated to the amino surface groups of the respective NPs. Efficient radiolabeling of NOTA-functionalized NPs with the positron emitter 64Cu was found. The biodistribution and PET studies showed a rapid renal clearance from the in vivo systems for both variants of the nanoparticles. Interestingly, the different derivatives investigated exhibited significant differences in the biodistribution and pharmacokinetic properties. This can mostly be attributed to different surface charge and hydrophilicity of the NPs, arising from the synthetic strategy used to prepare the particles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...