A sensitive calorimetric technique to study energy (heat) exchange at the nano-scale†
Abstract
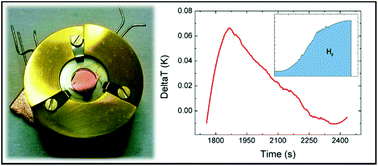
Every time a chemical reaction occurs, an energy exchange between reactants and the environment takes place, which is defined as the enthalpy of the reaction. During the last few decades, research has resulted in an increasing number of devices at the micro- or nano-scale. Sensors, catalyzers, and energy storage systems are more and more developed as nano-devices which represent the building blocks for commercial “macroscopic” objects. A general method for the direct evaluation of the energy balance of such systems is not available at present. Calorimetry is a powerful tool to investigate energy exchange, but it usually requires macroscopic sample quantities. Here, we report on the development of an original experimental setup able to detect temperature variations as low as 10 mK in a sample of ∼10 ng using a thermometer device having physical dimensions of 5 × 5 mm2. This technique has been utilized to measure the enthalpy release during the adsorption process of H2 on titanium-decorated monolayer graphene. The sensitivity of these thermometers is high enough to detect a hydrogen uptake of ∼10−10 moles, corresponding to ∼0.2 ng, with an enthalpy release of about 23 μJ. The experimental setup allows, in perspective, scalability to even smaller sizes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...