The flexoelectric effect in Al-doped hafnium oxide†
Abstract
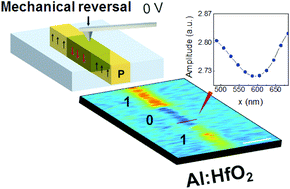
After the successful introduction as a replacement for the SiO2 gate dielectric in metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors, HfO2 is currently one of the most studied binary oxide systems with ubiquitous applications in nanoelectronics. For years, the interest of microelectronic downscaling has focused on tuning the dielectric constant of HfO2, particularly for monoclinic and tetragonal phases. Recently, Müller et al. showed the occurrence of ferroelectricity in orthorhombic HfO2 obtained by doping with Si, Y or Al which can alter the centrosymmetric atomic structure of the elemental binary oxide. Ferroelectric HfO2 is characterized by a permanent electric dipole that can be reversed through the application of an external voltage. As all ferroelectrics, a strong coupling between the polarization and the deformation exists, a property which has allowed the development of piezoelectric sensors and actuators. However, ferroelectrics also show a coupling between the electrical polarization and the deformation gradient, defined as flexoelectricity. In essence, the free charge inside the material redistributes in response to strain gradients, inducing a net non-zero dipole moment, eventually reaching polarization reversal by the sole application of a mechanical stress. Here we show the flexoelectric effect in Al-doped hafnium oxide, using the tip of an atomic force microscope (AFM) to maximize the strain gradient at the nanometre scale. Our analysis indicates that pure mechanical force can be used for the local polarization control of sub-100 nm domains. Due to the full compatibility of HfO2 in the modern CMOS process, the discovery of flexoelectricity in hafnia paves the way for (1) nanoscopic memory bits that can be written mechanically and read electrically, (2) tip-induced reprogrammable ferroelectric-based logic and (3) electromechanical transducers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...