The enzyme-like catalytic activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles and its dependency on Ce3+ surface area concentration†
Abstract
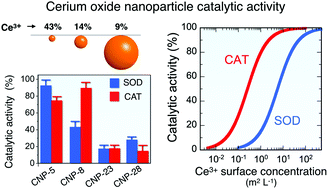
Cerium oxide nanoparticles are known to catalyze the decomposition of reactive oxygen species such as the superoxide radical and hydrogen peroxide. Herein, we examine the superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) mimetic catalytic activities of nanoceria and demonstrate the existence of generic behaviors. For particles of sizes 4.5, 7.8, 23 and 28 nm, the SOD and CAT catalytic activities exhibit the characteristic shape of a Langmuir isotherm as a function of cerium concentration. The results show that the catalytic effects are enhanced for smaller particles and for the particles with the largest Ce3+ fraction. The SOD-like activity obtained from the different samples is found to superimpose on a single master curve using the Ce3+ surface area concentration as a new variable, indicating the existence of particle independent redox mechanisms. For the CAT assays, the adsorption of H2O2 molecules at the particle surface modulates the efficacy of the decomposition process and must be taken into account. We design an amperometry-based experiment to evaluate the H2O2 adsorption at nanoceria surfaces, leading to the renormalization of the particle specific area. Depending on the particle type the amount of adsorbed H2O2 molecules varies from 2 to 20 nm−2. The proposed scalings are predictive and allow the determination of the SOD and CAT catalytic properties of cerium oxide solely from physicochemical features.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...