Friction and work function oscillatory behavior for an even and odd number of layers in polycrystalline MoS2†
Abstract
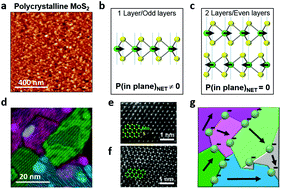
A large effort is underway to investigate the properties of two-dimensional (2D) materials for their potential to become building blocks in a variety of integrated nanodevices. In particular, the ability to understand the relationship between friction, adhesion, electric charges and defects in 2D materials is of key importance for their assembly and use in nano-electro-mechanical and energy harvesting systems. Here, we report on a new oscillatory behavior of nanoscopic friction in continuous polycrystalline MoS2 films for an odd and even number of atomic layers, where odd layers show higher friction and lower work function. Friction force microscopy combined with Kelvin probe force microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy demonstrates that an enhanced adsorption of charges and OH molecules is at the origin of the observed increase in friction for 1 and 3 polycrystalline MoS2 layers. In polycrystalline films with an odd number of layers, each crystalline nano-grain carries a dipole due to the MoS2 piezoelectricity, therefore charged molecules adsorb at the grain boundaries all over the surface of the continuous MoS2 film. Their displacement during the sliding of a nano-size tip gives rise to the observed enhanced dissipation and larger nanoscale friction for odd layer-numbers. Similarly, charged adsorbed molecules are responsible for the work function decrease in odd layer-number.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...