Lipid composition dictates serum stability of reconstituted high-density lipoproteins: implications for in vivo applications†
Abstract
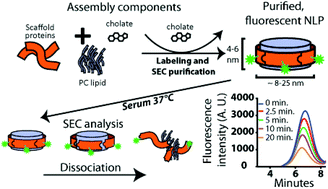
Nanolipoprotein particles (NLPs) are reconstituted high-density lipoproteins, consisting of a phospholipid bilayer stabilized by an apolipoprotein scaffold protein. This class of nanoparticle has been a vital tool in the study of membrane proteins, and in recent years has been increasingly used for in vivo applications. Previous work demonstrated that the composition of the lipid bilayer component affects the stability of these particles in serum solutions. In the current study, NLPs assembled with phosphatidylcholine lipids featuring different acyl chain structures were systematically tested to understand the effect that lipid composition has on NLP stability in both neat serum and cell culture media supplemented with 10% serum by volume. The time at which 50% of the particles dissociate, as well as the fraction of the initial population that remains resistant to dissociation, were correlated to key parameters obtained from all-atom simulations of the corresponding lipid bilayers. A significant correlation was observed between the compressibility modulus of the lipid bilayer and particle stability in these complex biological milieu. These results can be used as a reference to tune the stability of these versatile biological nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...