Using PEGylated magnetic nanoparticles to describe the EPR effect in tumor for predicting therapeutic efficacy of micelle drugs†
Abstract
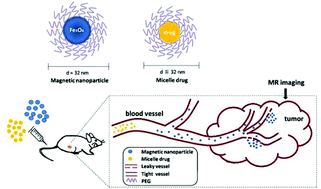
Micelle drugs based on a polymeric platform offer great advantages over liposomal drugs for tumor treatment. Although nearly all of the nanomedicines approved in the clinical use can passively target to the tumor tissues on the basis of an enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, the nanodrugs have shown heterogenous responses in the patients. This phenomenon may be traced back to the EPR effect of tumor, which is extremely variable in the individuals from extensive studies. Nevertheless, there is a lack of experimental data describing the EPR effect and predicting its impact on therapeutic efficacy of nanoagents. Herein, we developed 32 nm magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MION) as a T2-weighted contrast agent to describe the EPR effect of each tumor by in vivo magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The MION were synthesized by a thermal decomposition method and modified with DSPE-PEG2000 for biological applications. The PEGylated MION (Fe3O4@PEG) exhibited high r2 of 571 mM−1 s−1 and saturation magnetization (Ms) of 94 emu g−1 Fe as well as long stability and favorable biocompatibility through the in vitro studies. The enhancement intensities of the tumor tissue from the MR images were quantitatively measured as TNR (Tumor/Normal tissue signal Ratio) values, which were correlated with the delay of tumor growth after intravenous administration of the PLA-PEG/PTX micelle drug. The results demonstrated that the group with the smallest TNR values (TNR < 0.5) displayed the best tumor inhibitory effect. In addition, there was a superior correlation between TNR value and relative tumor delay in individual mice. These analysis results indicated that the TNR value of the tumor region enhanced by Fe3O4@PEG (d = 32 nm) could be used to predict the therapeutic efficacy of the micelle drugs (d ≤ 32 nm) in a certain period of time. Fe3O4@PEG has a potential to serve as an ideal MRI contrast agent to visualize the EPR effect in patients for accurate medication guidance of micelle drugs in the future treatment of tumors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...