Recombinant phosphatidylserine-binding nanobodies for targeting of extracellular vesicles to tumor cells: a plug-and-play approach†
Abstract
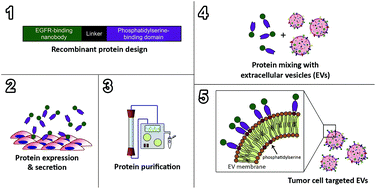
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are increasingly being recognized as candidate drug delivery systems due to their ability to functionally transfer biological cargo between cells. However, manipulation of targeting properties of EVs through engineering of the producer cells can be challenging and time-consuming. As a novel approach to confer tumor targeting properties to isolated EVs, we generated recombinant fusion proteins of nanobodies against the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) fused to phosphatidylserine (PS)-binding domains of lactadherin (C1C2). C1C2-nanobody fusion proteins were expressed in HEK293 cells and isolated from culture medium with near-complete purity as determined by SDS-PAGE. Fusion proteins specifically bound PS and showed no affinity for other common EV membrane lipids. Furthermore, C1C2 fused to anti-EGFR nanobodies (EGa1-C1C2) bound EGFR with high affinity and competed with binding of its natural ligand EGF, as opposed to C1C2 fused to non-targeting control nanobodies (R2-C1C2). Both proteins readily self-associated onto membranes of EVs derived from erythrocytes and Neuro2A cells without affecting EV size and integrity. EV-bound R2-C1C2 did not influence EV–cell interactions, whereas EV-bound EGa1-C1C2 dose-dependently enhanced specific binding and uptake of EVs by EGFR-overexpressing tumor cells. In conclusion, we developed a novel strategy to efficiently and universally confer tumor targeting properties to PS-exposing EVs after their isolation, without affecting EV characteristics, circumventing the need to modify EV-secreting cells. This strategy may also be employed to decorate EVs with other moieties, including imaging probes or therapeutic proteins.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...