Electrospray deposition of structurally complex molecules revealed by atomic force microscopy
Abstract
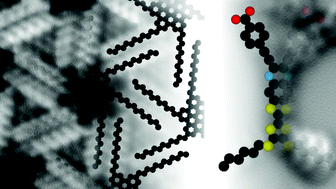
Advances in organic chemistry allow the synthesis of large, complex and highly functionalized organic molecules having potential applications in optoelectronics, molecular electronics and organic solar cells. Their integration into devices as individual components or highly ordered thin-films is of paramount importance to address these future prospects. However, conventional sublimation techniques in vacuum are usually not applicable since large organic compounds are often non-volatile and decompose upon heating. Here, we prove by atomic force microscopy and scanning tunneling microscopy, the structural integrity of complex organic molecules deposited onto an Au(111) surface using electrospray ionisation deposition. High resolution AFM measurements with CO-terminated tips unambiguously reveal their successful transfer from solution to the gold surface in ultra-high vacuum without degradation of their chemical structures. Furthermore, the formation of molecular structures from small islands to large and highly-ordered self-assemblies of those fragile molecules is demonstrated, confirming the use of electrospray ionisation to promote also on-surface polymerization reactions of highly functionalized organic compounds, biological molecules or molecular magnets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...