Ag-Functionalized CuWO4/WO3 nanocomposites for solar water splitting†
Abstract
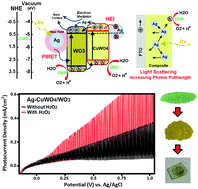
Ag-Functionalized CuWO4/WO3 heterostructures were successfully prepared via a polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP)-assisted sol–gel (PSG) route. Thin films prepared via electrophoretic deposition were used as photoanodes for photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting. Compared to pristine CuWO4 and WO3 films, a significant enhancement of the photocurrent (3–4 times) at the thermodynamic potential for oxygen evolution (0.62 V vs. Ag/AgCl, pH 7) was obtained for the Ag-functionalized CuWO4/WO3 photoanodes. The obtained enhancement is shown to be derived from a synergic contribution of heterostructure formation (CuWO4/WO3) and improvements of light utilization by Ag-induced surface plasmon resonance (SPR) effects. Accordingly, a photocurrent of 0.205 mA cm−2 at 0.62 V vs. Ag/AgCl under neutral conditions (without hole scavengers) under front-side simulated AM1.5G illumination was achieved. A detailed analysis of the obtained PEC data alongside performed impedance measurements suggests that charge seperation is significantly improved for the prepared Ag-functionalized CuWO4/WO3 photoanodes. Our work offers beneficial insights to design new plasmonic metal/heterostructured nanocomposites for energy conversion applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...