Bi2WO6/Ag3PO4–Ag Z-scheme heterojunction as a new plasmonic visible-light-driven photocatalyst: performance evaluation and mechanism study†
Abstract
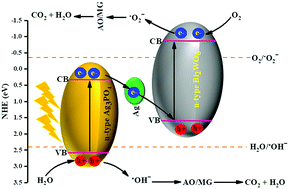
The Bi2WO6/Ag3PO4–Ag Z-scheme heterojunction, as a novel plasmonic visible-light-driven photocatalyst, was prepared by ultrasound assisted in situ precipitation and the hydrothermal method and was further characterized using multiple techniques. The photocatalytic performance of the synthesized Z-scheme heterojunction was evaluated by degradation of a binary mixture of organic pollutants dyes. The results revealed the superior photocatalytic activity was due to the decrease of the electron–hole pair recombination rate, as well as the enhancement of the diffusion rate of the electrons and holes across the Bi2WO6/Ag3PO4/Ag Z-scheme heterojunction interfaces. The synergistic effects of the Ag nanoparticles in the Bi2WO6/Ag3PO4–Ag Z-scheme heterojunction could improve the photo-stability, as well as the recyclability, towards dyes decomposition owing to their contribution to the separation of electron–hole pairs resulting from the formation of the Z-scheme heterojunction. This work presents a promising strategy for the preparation of novel photocatalysts with high separation efficiency of charge carriers, providing a new concept for the rational design and development of highly efficient photocatalysts. Central composite design (CCD) based on response surface methodology (RSM) was applied to investigate the optimization of the operational parameters on the degradation efficiency as well. The results indicated that compared to pure Bi2WO6 and Ag3PO4, Bi2WO6/Ag3PO4–Ag has a superior photodegradation efficiency of 86.90% and 82.04% for MG and AO degradation, respectively. The effect of the operational parameters, including the initial MG concentration (4–12 mg L−1), AO concentration (2–6 mg L−1), photocatalyst mass (0.008–0.016 g), irradiation time (60–120 min) and pH (3–9), on the degradation efficiency was investigated and the optimized values were found to be pH 6.057, an MG concentration of 8.0769 mg L−1, an AO concentration of 4.038 mg L−1, 0.012 g of Bi2WO6/Ag3PO4–Ag and 90.57 min of irradiation time. Finally, a photocatalytic degradation mechanism is proposed and the separation of the electron–hole pairs resulting from the formation of the Z-scheme heterojunction with Ag as a plasmonic electron mediator is discussed in detail.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...