Nickel nanoparticles grown by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method for ethanol electrooxidation and electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance study†
Abstract
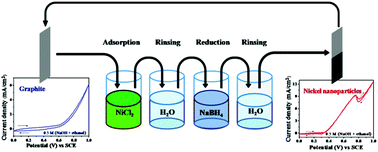
Nickel nanoparticles were grown on graphite by using a comparatively simpler and cost effective method, namely successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction. Size and morphology of the nickel nanoparticles were observed using field emission scanning electron microscopy. X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy studies confirmed the presence of nickel. Electrocatalytic activity and stability of the grown nickel nanoparticles were investigated by recording cyclic voltammograms and chronoamperometry. Variations in growth parameters, such as reduction time, nickel chloride concentration and number of growth cycles affect the activity of the grown nickel nanoparticles. The grown nickel nanoparticles exhibited electrocatalytic activity towards ethanol electrooxidation reaction. The phase change as a result of mass change that occurred during the redox reactions and ethanol electrooxidation was studied using an electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance. The successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method promises to be a viable option for growth of nickel nanoparticles for electrocatalytic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...