Pyrophosphate effect on the photocatalytic degradation of phenol over bare and Pt-deposited Bi2WO6†
Abstract
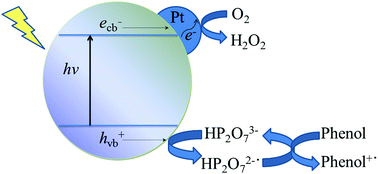
Pyrophosphate anions (PPA) are widely present in wastewater, but their effect on semiconductor photocatalyis for organic degradation has not been established yet. In this study, we report a synergistic effect between Pt and PPA, that greatly improves photocatalytic activity of Bi2WO6 (BiW) for phenol degradation in aqueous solutions at pHs 5–11. BiW was synthesized by a hydrothermal method, followed by photochemical deposition of 0.5% Pt (Pt/BiW). Upon addition of PPA, rates of phenol degradation on BiW and Pt/BiW decreased and increased, respectively. The former is due to decreased O2 adsorption, as inferred from photocatalytic and electrochemical reductions of O2. (Photo)electrochemical measurements revealed that Pt and PPA act as electron and hole mediators, respectively. It is proposed that adsorbed PPA on the catalyst is first oxidized to a pyrophosphate anion radical, followed by phenol oxidation to regenerate PPA. However, as PPA concentration increased beyond 0.50 mM, rate of phenol degradation on Pt/BiW started to decrease, due to self-recombination of pyrophosphate anion radicals into a less reactive product.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...