SERS effect of selectively adsorbed dyes by hydrothermally-produced MoS2 nanosheets†
Abstract
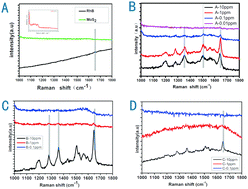
The electro-magnetic mechanism and chemical transfer mechanism coexist in the surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) procedure. However, the latter is regretfully neglected due to the poor chemical transfer efficiency without the aid of a direct chemical bond. Herein, to further explore the CM Raman enhancement and understand the mechanism of SERS, Raman testing and the adsorption experiment have been carried out with respect to the exploration and application of metal-free SERS substrate. Thus, functional organic group-modified MoS2 nanosheets have been prepared via the hydrothermal method, and this as-prepared MoS2 shows an apparent Raman signal enhancement effect when serving/as the Raman substrate. Compared with those without organic groups (purchased MoS2) and those with one organic group removed (annealed MoS2), it is found that the minimum detection concentration of Rhodamine B (RhB) with the as-prepared functional MoS2 nanosheets could be 0.1 ppm, while the detection limit of annealed as-prepared MoS2 nanosheets and commercially purchased MoS2 powders were only 1 ppm and 10 ppm, respectively. Fourier transition infrared spectroscopy has revealed that the surface of the as-prepared MoS2 nanosheets was passivated by –NH2 and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C and C
C and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O groups. The lone pair electrons in –NH2 and the p-bond electrons in C
O groups. The lone pair electrons in –NH2 and the p-bond electrons in C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C and C
C and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O groups would coordinate the nitrogen ethyl of RhB, forming a direct chemical bond, which could significantly contribute to the charge transfer. This led to efficient adsorption of the RhB molecule, which is key to achieving the SERS effect with the prepared MoS2 nanosheets substrate.
O groups would coordinate the nitrogen ethyl of RhB, forming a direct chemical bond, which could significantly contribute to the charge transfer. This led to efficient adsorption of the RhB molecule, which is key to achieving the SERS effect with the prepared MoS2 nanosheets substrate.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...