Aggregation behavior of sodium 3-(octyloxy)-4-nitrobenzoate in aqueous solution
Abstract
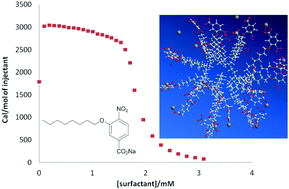
Ester 3-(octanoyloxy)-4-nitrobenzoic acid is a standard for the assay of the activity of phospholipase enzymes (the main toxins involved in tissue-damaging after snake bites). Because of its amphiphilic nature, it probably behaves as a surfactant but the instability of the ester bond prevents its characterization. Its ether analogue, 3-(octyloxy)-4-nitrobenzoic acid, is also an interesting compound as it is an inhibitor of the phospholipase activity and can be accepted as a model of the ester derivative. Its sodium salt, stable at basic pH, was studied by surface tension measurements, isothermal titration calorimetry, dynamic light scattering (DLS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The aggregation number, fraction of bound counterions, critical micelle concentration and thermodynamic parameters involved in demicellization were obtained. The positive value for the change in the heat capacity for demicellization indicates that a larger hydrophobic surface area of each monomer is exposed to a hydrophilic environment after dissociation. Semiempirical calculations are in agreement with DLS and TEM measurements. For several carboxylate surfactants, the plot of enthalpy vs. entropy is linear. Although the slope has been named the compensation temperature, Tc, it merely is an experimental temperature without any extra-thermodynamic meaning.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...