Hydrogen bonded networks based on hexarhenium(iii) chalcocyanide cluster complexes: structural and photophysical characterization†
Abstract
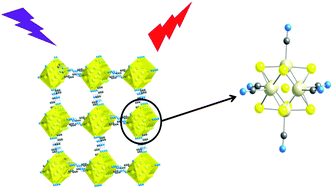
Two series of isostructural compounds resulting from the combination of the four-fold hydrogen bond donors bisamidinium cations, namely 1-2H+ and 2-2H+, and the anionic chalcocyanide clusters of general formula [Re6Qi8(CN)a6]4− are presented (Q = S or Se; where i and a denote inner and apical position, respectively). 1-2H+ is built upon two imidazolium groups linked together by a –(CH2)2– alkyl chain. 2-2H+ is built upon two hydroxyamidinium groups linked together via a phenyl group and, in consequence, it exhibits a planar geometry. This ionic association leads to either two or three-dimensional hydrogen-bonded networks in the solid state, as confirmed by X-ray crystallographic analysis. The solid-state structures arise from the recognition between the pendant –C![[triple bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e002.gif) N ligands of the cluster cores and the amidinium H-bond donors. The luminescence properties of the compounds are investigated in the solid state by means of steady-state and time-resolved techniques. Results are discussed and compared with those measured for the parent Cs4[Re6Si8(CN)a6] and Cs4[Re6Sei8(CN)a6] species. The H-bonded networks display featureless deep-red emission bands centered at λem = 722 and 737 nm and average excited-state lifetimes ranging between 11.5 and 14.8 μs, in accordance with the triplet nature of the radiative process. These photoluminescence properties are similar to the Cs+ homologues and are attributed to the [Re6Qi8]2+ emitting core.
N ligands of the cluster cores and the amidinium H-bond donors. The luminescence properties of the compounds are investigated in the solid state by means of steady-state and time-resolved techniques. Results are discussed and compared with those measured for the parent Cs4[Re6Si8(CN)a6] and Cs4[Re6Sei8(CN)a6] species. The H-bonded networks display featureless deep-red emission bands centered at λem = 722 and 737 nm and average excited-state lifetimes ranging between 11.5 and 14.8 μs, in accordance with the triplet nature of the radiative process. These photoluminescence properties are similar to the Cs+ homologues and are attributed to the [Re6Qi8]2+ emitting core.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...