A novel high-capacity immunoadsorbent with PAMAM dendritic spacer arms by click chemistry†
Abstract
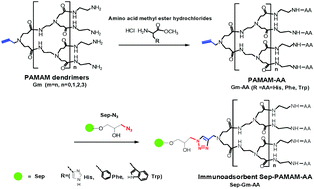
Polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers, bearing multiple peripheral end groups that can be used as clickable modules, make it possible to bind a large number of small-molecule ligands via click chemistry to prepare high-capacity immunoadsorbents. Thus, an immunoadsorbent with PAMAM dendritic spacer arms possessing pseudo-biospecific affinity for IgG from human plasma, Sep-PAMAM-AA, was designed and prepared by click chemistry using sepharose gel as a support and the amino acids His, Phe and Trp as ligands; two sepharose-based control samples, Sep-triazole-His and Sep-PA, with linear spacer arms were prepared using L-histidine and protein A as ligands, respectively. The ligand density and IgG adsorption performance of Sep-PAMAM-AA from human plasma were measured and evaluated. The influences of the structure and generation number of the PAMAM spacer arms on the performances of the products were also investigated. The results indicate that the immunoadsorbent with PAMAM G3 as a spacer arm and His as a ligand, Sep-G3-His, is the best among the prepared immunoadsorbents. Its ligand density reaches 1.58 mmol g−1 sepharose gel, almost 5-fold higher than that of Sep-triazole-His; its IgG adsorption capacity is 28.43 mg g−1, which is higher than those of Sep-triazole-His and Sep-PA. Moreover, Sep-G3-His exhibits a relatively low level of non-specific adsorption, which indicates that the immunoadsorbents with PAMAM as a spacer arm and His as a ligand are expected to have great application prospects in the field of blood purification.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...