Construction of a solar spectrum active SnS/ZnO p–n heterojunction as a highly efficient photocatalyst: the effect of the sensitization process on its performance†
Abstract
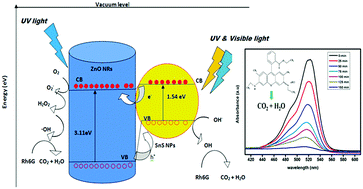
In this paper, we present a highly efficient SnS nanoparticle sensitized zinc oxide (ZnO) nanorod based photocatalyst, which can degrade strong organic dyes under direct exposure to sunlight. The thermal decomposition technique was adopted to prepare crystalline ZnO nanorods, which were subsequently sensitized with a narrow bandgap semiconductor, namely tin sulfide (SnS), via in situ and ex situ sensitization processes. Here, SnS acts as a photosensitizer to expand the light absorption range from the UV-VIS-NIR spectral region. In addition, the formation of the SnS/ZnO heterostructure suppresses the electron–hole pair recombination via the formation of a p–n heterojunction and enhances the separation of photoexcited charge carriers. Thereafter, the photocatalytic activity of the pristine ZnO nanorods and sensitized SnS/ZnO nanorods was investigated in the degradation of three different strong dyes under sunlight illumination. It was observed that the in situ sensitization process helps in achieving a uniform coating of SnS over the surface of the ZnO nanorods, which resulted in an enhanced photocatalytic performance in dye degradation in comparison to the ex situ sensitized SnS/ZnO nanorods and pristine ZnO nanorods. The rate constants for the in situ sensitized SnS/ZnO nanorods determined from experimental data were found to be 0.0245 min−1, 0.0212 min−1 and 0.0139 min−1 in the photodegradation of Rhodamine 6G, Rhodamine B, and Methyl Orange dyes, respectively. Thus, we can infer from our experimental results that the in situ sensitized SnS/ZnO nanorods could be an economical and promising inorganic photocatalytic material, in addition to the TiO2 photocatalyst for photodegradation of toxic organic dyes present in water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...