Chiral electrochemical recognition of tryptophan enantiomers at a multi-walled carbon nanotube–N-carboxymethyl chitosan composite-modified glassy carbon electrode†
Abstract
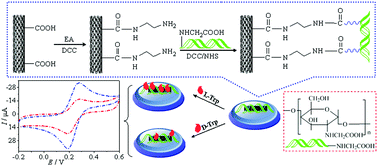
A simple chiral electrochemical sensor based on N-carboxymethyl chitosan (NCCS) covalently bound with ethylenediamine-carboxylic multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs-EA) was developed for enantioselective recognition of tryptophan (Trp) enantiomers; NCCS preferably combined with L-Trp than with D-Trp. The recognition efficiency prominently increased after the introduction of N-carboxymethyl into chitosan (CS). The carboxymethyl and imino groups of NCCS play an important role in enantioselective discrimination system. Moreover, the parameters of enantioselective recognition such as pH, temperature and response time were investigated. The electrochemical recognition of amino acid enantiomers with different functional groups was carried out. The chiral recognition mechanism was investigated by quantum computing. The results were confirmed by quantum chemical calculations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...