Visible-enhanced photocatalytic performance of CuWO4/WO3 hetero-structures: incorporation of plasmonic Ag nanostructures
Abstract
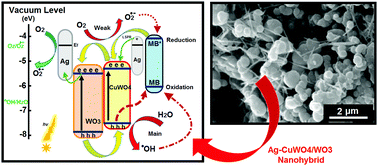
A new plasmonic Ag hybridized CuWO4/WO3 heterostructure was successfully synthesized via a ligand-assisted sol gel method. The as-prepared plasmonic nanohybrid was thoroughly characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV-visible spectroscopy, photoluminescence (PL) spectrometry, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Raman spectroscopy, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area analysis and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Moreover, the photocatalytic activity was evaluated by photo-degradation of methylene blue (MB) under visible light irradiation. The results indicate that the as-prepared plasmonic Ag–CuWO4/WO3 nanohybrid (compared to pure WO3) with high surface area exhibits significant enhancement in photocatalytic behavior in the visible spectrum, which can be ascribed to combined effects, including the more effective absorption of visible light, lower bulk resistance, effective separation/transfer of photo-generated charge carriers and reduced electron/hole recombination which results from the contribution of hetero-junction and plasmonic Ag incorporation. In addition, a possible mechanism for the photo-degradation process of the hetero-structured Ag nanohybrid is proposed. Finally, the metal/semiconductor nanohybrid displayed sufficient recyclability with respect to photocatalytic activity, making it a promising candidate for pollutant degradation and energy conversion applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...